Education - Part 5A4
Motive Power - Steam Power
Motive Power - Steam Power
Steam Locomotive
The steam locomotive is a marvel of engineering. Although very largely historical at this point in time, it is instructive to study the basics of steam locomotives.
Steam-powered locomotives convert steam energy to mechanical energy by boiling water to produce steam. Liquid water increases in volume by about 1700 times at standard temperature and pressure (STP) when it changes to the gaseous state and it is this change in volume that creates a mechanical advantage.
Steam (gaseous water) produced in a boiler is piped to a cylinder containing a piston. This forces the piston to move. By linking the piston to an axel, the movement of the piston is translated into a movement of the axel. If the axel is fitted with wheels at opposite ends, the wheels will rotate, thus achieving motion along a predetermined path. If the cylinder containing the piston can be fed steam at either end, a continuous forward movement of the linked wheels can be achieved. That is the essence of operation of a steam-powered locomotive. Examples of steam-powered locomotives on the Shannondell Model Railroad may be found here.
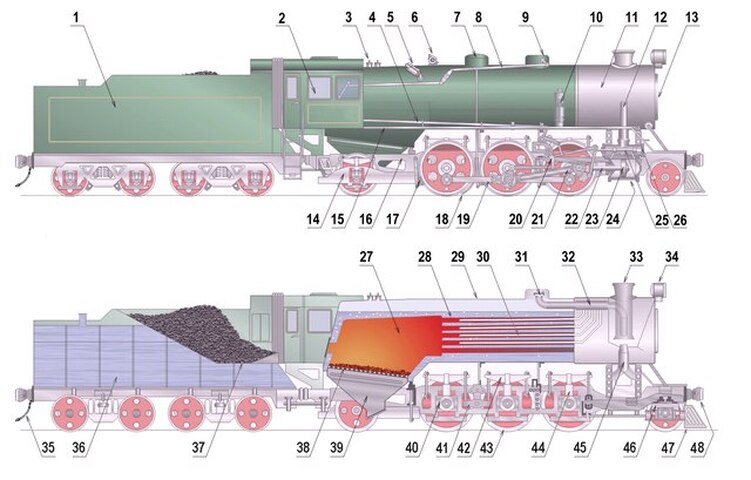
Every steam locomotive consisted of a frame upon which to support a fire box that heated water to steam in a boiler, a cab in which the driver and support staff worked, a set of wheels upon which these components rested, plumbing, control mechanisms and other components. The following illustration identifies 48 different but integrated components of a steam locomotive.
The steam locomotive is a marvel of engineering. Although very largely historical at this point in time, it is instructive to study the basics of steam locomotives.
Steam-powered locomotives convert steam energy to mechanical energy by boiling water to produce steam. Liquid water increases in volume by about 1700 times at standard temperature and pressure (STP) when it changes to the gaseous state and it is this change in volume that creates a mechanical advantage.
Steam (gaseous water) produced in a boiler is piped to a cylinder containing a piston. This forces the piston to move. By linking the piston to an axel, the movement of the piston is translated into a movement of the axel. If the axel is fitted with wheels at opposite ends, the wheels will rotate, thus achieving motion along a predetermined path. If the cylinder containing the piston can be fed steam at either end, a continuous forward movement of the linked wheels can be achieved. That is the essence of operation of a steam-powered locomotive. Examples of steam-powered locomotives on the Shannondell Model Railroad may be found here.
Every steam locomotive consisted of a frame upon which to support a fire box that heated water to steam in a boiler, a cab in which the driver and support staff worked, a set of wheels upon which these components rested, plumbing, control mechanisms and other components. The following illustration identifies 48 different but integrated components of a steam locomotive.
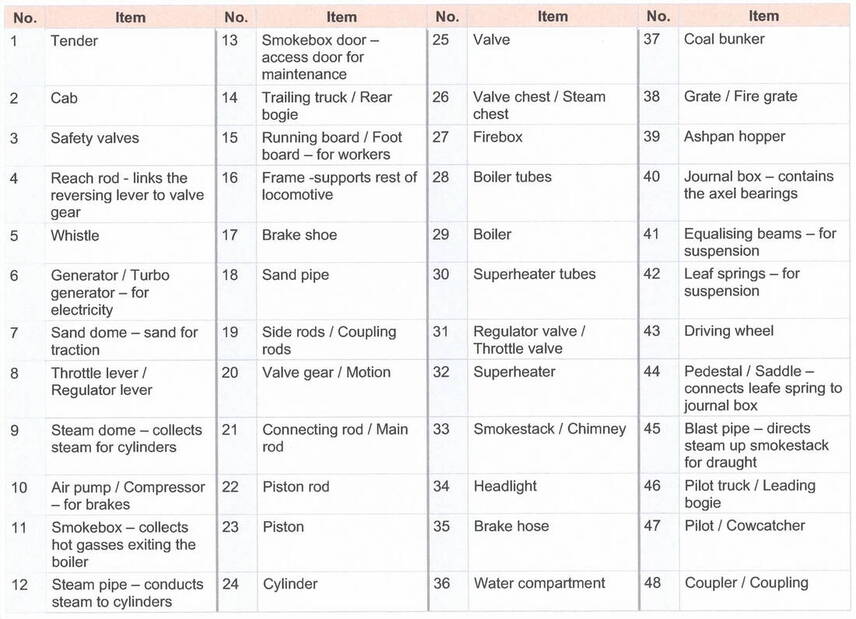
A description of the numbered components (above) is given in the following table.
Although steam-powered locomotives were used for many years, the only remaining operating examples are used in tourist applications (e.g., excursion trains) giving people a chance to experience them once again. Some can also be found in museums.
No steam-powered locomotive could meet the current regulations for environmental care and probably not safety and health regulations either. There is an instructive video (17:16 minutes) showing how a steam locomotive was built in 1935. It is well worth watching.
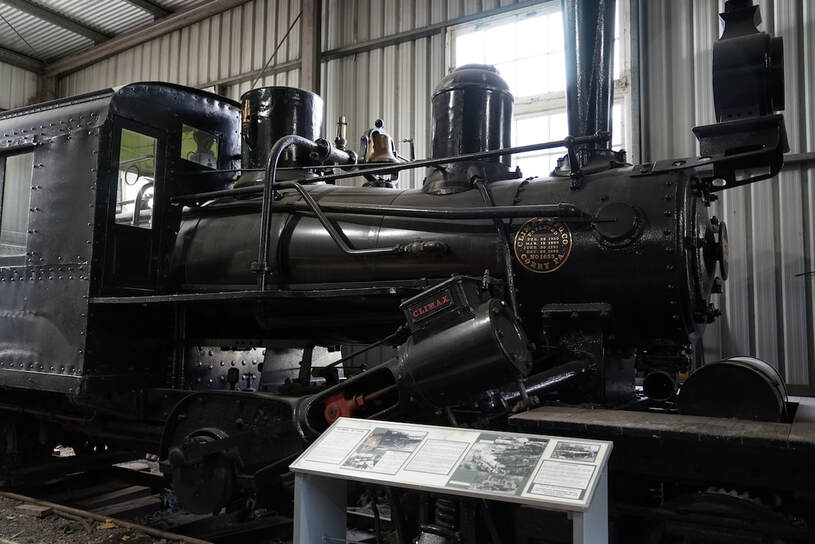
The following image is of a steam locomotive built by Climax Manufacturing Co. in Curry, PA in 1923.
No steam-powered locomotive could meet the current regulations for environmental care and probably not safety and health regulations either. There is an instructive video (17:16 minutes) showing how a steam locomotive was built in 1935. It is well worth watching.
The following image is of a steam locomotive built by Climax Manufacturing Co. in Curry, PA in 1923.
Steam Turbine Locomotive
Steam Turbine Locomotives are once again in the news (https://www.railadvent.co.uk/2024/06/class-60-diesel-locomotive-set-to-be-powered-by-steam-in-new-trial.html) as a solution of one or more problems faced by the railroad industry, namely tractive effort for freight (goods) trains and reduction of carbon pollution. The first problem stems from the cost of electrification of existing rail lines. Various solutions are in play, including diesel electric locomotives that replaced steam locomotives (see below) beginning around 1930 but more successfully by 1950, battery-based electric locomotives entering the fray today and steam turbine locomotives.
The second problem stems from the need to reduce carbon emissions to an absolute minimum. Diesel-electric locomotives produce substantially less harmful exhaust than traditional steam locomotives and electric locomotives emit no (or miniscule) carbon dioxide, but they suffer from the difficulty of delivering electric energy to the locomotive. Battery storage of electric energy is one solution and other solutions have been proposed or tried (see Other Power).
Steam turbines were first developed in 1884 by Charles Parsons [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steam_turbine]. A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft (https://www.nuclear-power.com/nuclear-power-plant/turbine-generator-power-conversion-system/what-is-steam-turbine-description-and-characteristics/). The output shaft may directly drive a ship or locomotive through direct mechanical connection to a propeller or set of driving wheels, but is more likely to be used to turn an electric generator, the output of which is used to power an electric motor that moves the object of interest. In fact, as much as 90% of the electric energy we use today is produced by turbine engines, many of which are steam turbines. However, much of the steam that drives these engines is produced by burning fossil fuels such as coal or oil and this contributes significantly to global warming. For more about steam and gas turbine locomotives, see https://www.steamlocomotive.com/types/turbine/.
A group of companies (Eversholt Rail (https://eversholtrail.co.uk), Steamology (https://www.steamology.co.uk), Arup (https://www.arup.com) and Freightliner (https://www.freightliner.co.uk)) is working to transform a Class 60 diesel-electric locomotive (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_Rail_Class_60) to one powered by steam turbines [https://www.railwaygazette.com/uk/steam-turbine-freight-locomotive-prototype-to-be-developed/66715.article].The effort is financed by Innovate UK (https://www.ukri.org/councils/innovate-uk/).
The design calls for 20 steam generators, four steam turbines and 140kg of gas (hydrogen) storage capacity that will replace the diesel engine in the prototype. The steam generators are powered by burning hydrogen, which produces water as the exhaust. The steam produced will drive steam turbines that will drive generators that supply electrical energy to the traction motors. A working prototype is expected in 2025. If successful, stem power may once again ride the rails.
Steam Turbine Locomotives are once again in the news (https://www.railadvent.co.uk/2024/06/class-60-diesel-locomotive-set-to-be-powered-by-steam-in-new-trial.html) as a solution of one or more problems faced by the railroad industry, namely tractive effort for freight (goods) trains and reduction of carbon pollution. The first problem stems from the cost of electrification of existing rail lines. Various solutions are in play, including diesel electric locomotives that replaced steam locomotives (see below) beginning around 1930 but more successfully by 1950, battery-based electric locomotives entering the fray today and steam turbine locomotives.
The second problem stems from the need to reduce carbon emissions to an absolute minimum. Diesel-electric locomotives produce substantially less harmful exhaust than traditional steam locomotives and electric locomotives emit no (or miniscule) carbon dioxide, but they suffer from the difficulty of delivering electric energy to the locomotive. Battery storage of electric energy is one solution and other solutions have been proposed or tried (see Other Power).
Steam turbines were first developed in 1884 by Charles Parsons [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steam_turbine]. A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft (https://www.nuclear-power.com/nuclear-power-plant/turbine-generator-power-conversion-system/what-is-steam-turbine-description-and-characteristics/). The output shaft may directly drive a ship or locomotive through direct mechanical connection to a propeller or set of driving wheels, but is more likely to be used to turn an electric generator, the output of which is used to power an electric motor that moves the object of interest. In fact, as much as 90% of the electric energy we use today is produced by turbine engines, many of which are steam turbines. However, much of the steam that drives these engines is produced by burning fossil fuels such as coal or oil and this contributes significantly to global warming. For more about steam and gas turbine locomotives, see https://www.steamlocomotive.com/types/turbine/.
A group of companies (Eversholt Rail (https://eversholtrail.co.uk), Steamology (https://www.steamology.co.uk), Arup (https://www.arup.com) and Freightliner (https://www.freightliner.co.uk)) is working to transform a Class 60 diesel-electric locomotive (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_Rail_Class_60) to one powered by steam turbines [https://www.railwaygazette.com/uk/steam-turbine-freight-locomotive-prototype-to-be-developed/66715.article].The effort is financed by Innovate UK (https://www.ukri.org/councils/innovate-uk/).
The design calls for 20 steam generators, four steam turbines and 140kg of gas (hydrogen) storage capacity that will replace the diesel engine in the prototype. The steam generators are powered by burning hydrogen, which produces water as the exhaust. The steam produced will drive steam turbines that will drive generators that supply electrical energy to the traction motors. A working prototype is expected in 2025. If successful, stem power may once again ride the rails.