Education - Part 5A9
Motive Power - Manufacturers
Motive Power - Manufacturers
Famous Locomotives
From the historical point of view, several locomotives have become famous for various reasons. Among them are the following:
Tom Thumb, designed and constructed in 1829 by Peter Cooper, was the first American-built steam locomotive to operate on a common-carrier, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O). It was intended to replace B&O's horse-drawn trains.
New York Central and Hudson River Railroad No. 999, a 4-4-0 “American” type steam locomotive, was built for the railroad in 1893 by New York Central West Albany Shops.
Pennsylvania Railroad 1361 is a 4-6-2 "Pacific"-type steam locomotive built in 1918 by the Pennsylvania Railroad's Altoona Works. See also "Pacific K4" under Railroad History.
From the historical point of view, several locomotives have become famous for various reasons. Among them are the following:
Tom Thumb, designed and constructed in 1829 by Peter Cooper, was the first American-built steam locomotive to operate on a common-carrier, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O). It was intended to replace B&O's horse-drawn trains.
New York Central and Hudson River Railroad No. 999, a 4-4-0 “American” type steam locomotive, was built for the railroad in 1893 by New York Central West Albany Shops.
Pennsylvania Railroad 1361 is a 4-6-2 "Pacific"-type steam locomotive built in 1918 by the Pennsylvania Railroad's Altoona Works. See also "Pacific K4" under Railroad History.
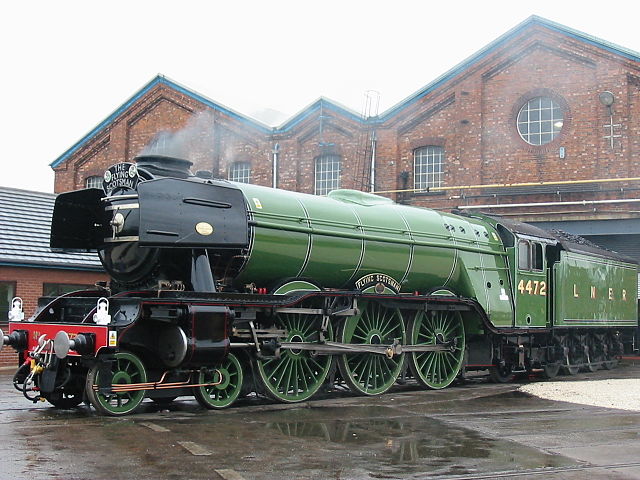
LNER Class A3 4472 Flying Scotsman is a 4-6-2 "Pacific" steam locomotive built in 1923 for the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) at Doncaster Works. It was employed on long-distance express service between London, England and Edinburgh, Scotland.
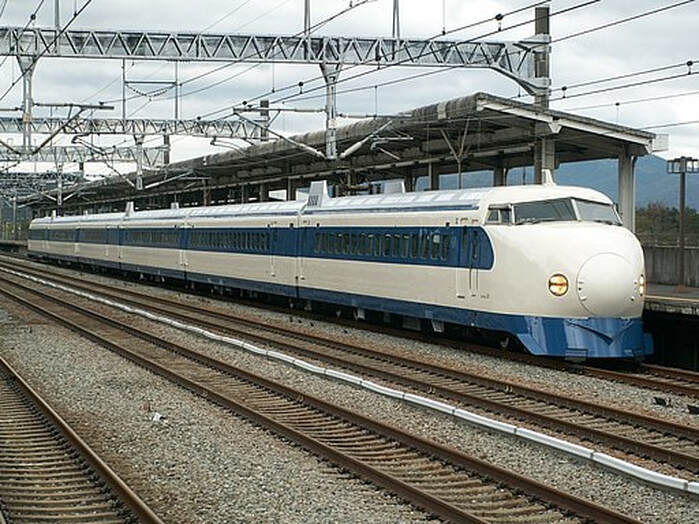
Japan Railways Shinkansen 1964. Starting with the Tōkaidō Shinkansen (515.4 km, 320.3 mi) in 1964, Japan introduced the era of fast trains (trains routinely operating at velocities of 125 mph (200 kmh or more). The Shinkansen is actually a train set, because all cars are built to operate as an integral unit. Trains of up to 16 cars may be used to handle the high volume of passenger traffic experienced (over 5.6 billion paying customers since inception). Today there are many Shinkansen running on five interconnected routes. These trains operate with extreme precision, allowing trains on a given line to be spaced as closely as 3 minutes apart.
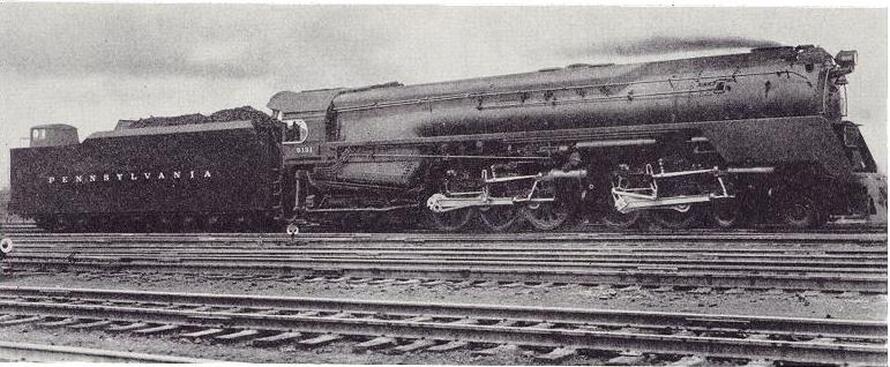
Among the largest and most powerful steam locomotives ever built were the following:
Pennsylvania Railroad non-articulated 4-4-6-4 Q2 class built at the Altoona Works;
Chesapeake and Ohio Railway H-8 "Allegheny" class and the Virginian Railway "Blue Ridge" class 2-6-6-6 built by Lima Locomotive Works;
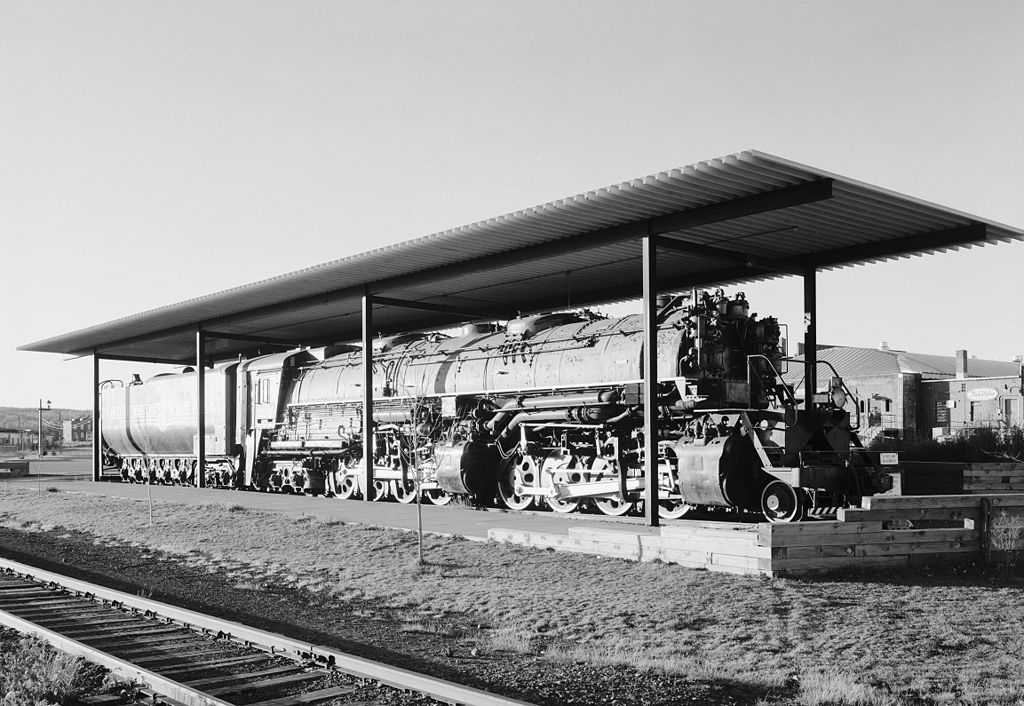
the 2-8-8-4 "Yellowstone" class built by American Locomotive Co. (ALCO) and Baldwin Locomotive Works for Northern Pacific Railway and Duluth, Missabe and Iron Range Railway (among others);
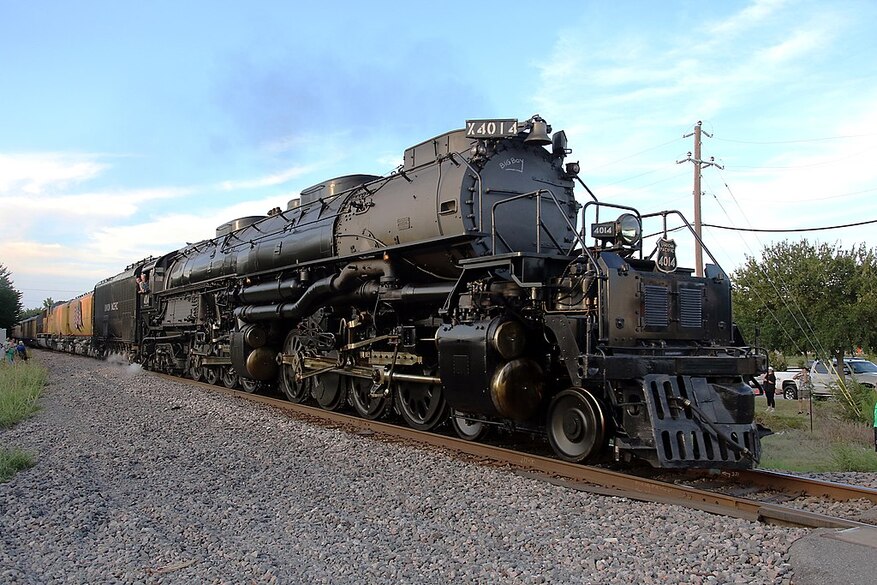
Union Pacific "Big Boy" class 4-8-8-4 articulated locomotives built by ALCO.
Examples of these locomotives are illustrated below.
Pennsylvania Railroad non-articulated 4-4-6-4 Q2 class built at the Altoona Works;
Chesapeake and Ohio Railway H-8 "Allegheny" class and the Virginian Railway "Blue Ridge" class 2-6-6-6 built by Lima Locomotive Works;
the 2-8-8-4 "Yellowstone" class built by American Locomotive Co. (ALCO) and Baldwin Locomotive Works for Northern Pacific Railway and Duluth, Missabe and Iron Range Railway (among others);
Union Pacific "Big Boy" class 4-8-8-4 articulated locomotives built by ALCO.
Examples of these locomotives are illustrated below.