Education - Part 5A5
Motive Power - Diesel-Electric Power
Motive Power - Diesel-Electric Power
Diesel-Electric Locomotive
The workhorse of the railroad industry today is the diesel-electric locomotive, especially in North America. These locomotives are electric because it is electric traction motors that drive the axels. They are diesel because it is a large diesel-powered engine that drives either a generator or alternator that produces the electricity upon which the traction motors depend. Gone are the massive drive wheels of the steam era, replaced by two or more trucks (bogies) of two or three axels (trucks will be described in more detail a bit later). A tender is replaced by a diesel fuel tank suspended from the locomotive frame.
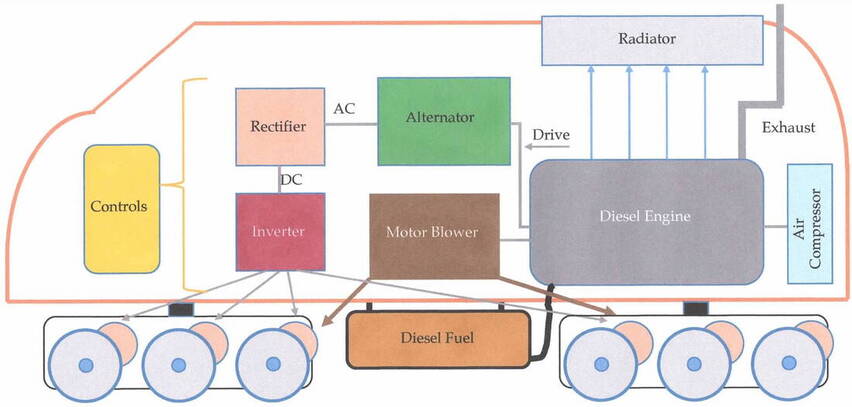
Within the body of the locomotive there is a diesel engine, the drive-shaft of which is coupled to either a generator (producing direct current or DC electric power) or an alternator (producing alternating current or AC electric power). Various other devices in the locomotive are also electrically powered, such as the operating controls, an air compressor for air brakes and other applications, a traction motor blower to help maintain the correct traction motor operating temperature and radiator fans to maintain the correct operating temperature of the diesel engine. These various devices, although essential, do not contribute to tractive effort and are thus called parasitic loads (an electrical load is anything energized by a source of electricity; in essence a consumer of electrical energy).
The following diagram illustrates the main components of a diesel-electric locomotive.
In this illustration, the diesel engine drives an alternator that produces alternating current (AC) at some desired voltage. This AC supply then passes through a rectifier that not only converts the AC to DC, it is also designed to smooth the current flow to yield a steady voltage. Once a steady voltage is achieved, the current passes through an inverter to produce AC once again. This power source drives the traction motors that move the locomotive. In the above illustration, the locomotive has two trucks (bogies) each with three axels (6 wheels). Each axel is rotated by means of gears turned by the traction motors that mesh with the gears on the axels. The trucks also carry a braking mechanism to slow or stop the locomotive.
Diesel-electric locomotives are much more efficient and environmentally friendly than steam-powered locomotives. The Environmental Protection Agency established Tier 4 performance standards for diesel-electric locomotives in 2015. General Electric Transportation (now part of Wabtec) began delivering a new line of such locomotives beginning in Autumn 2015. Today, the addition of battery-powered locomotives (see Other Motive Power below) further improves both environmental performance and overall fuel efficiency. The following photo shows an example of a diesel-electric locomotive.